

Analysis on the development prospect and investment scale of waste-to-energy industry in 2020
date:2020-05-12 11:57:39
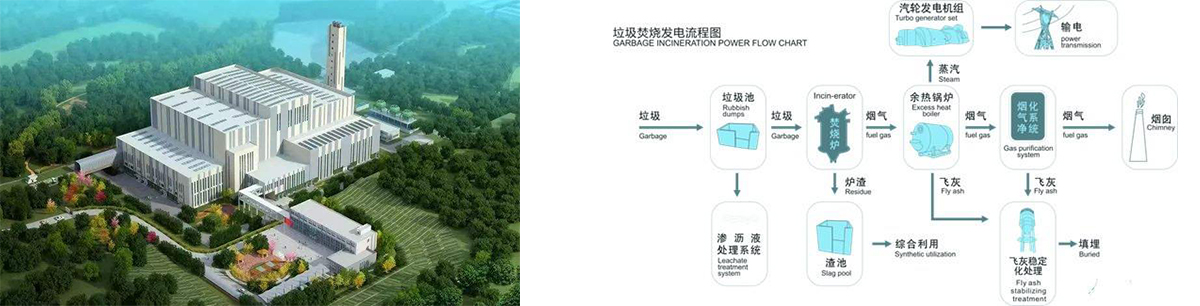
Waste-to-energy power generation refers to a form of power generation in which municipal solid waste is burned by a special incineration boiler and then generated by a steam turbine generator set. Waste-to-energy power generation is divided into two categories: waste incineration power generation and landfill gas power generation. In the face of faster and faster urbanization in the world, the proliferation of urban waste has become a major disaster in cities. Countries all over the world have not only limited to the passive "defense" tactics of burying and destroying garbage, but have actively taken effective measures to carry out comprehensive and scientific treatment of garbage. my country is rich in garbage resources and has great potential benefits. The annual loss of nearly 30 billion yuan (transportation fees, disposal fees, etc.) caused by garbage in cities across the country can create a benefit of 250 billion yuan by comprehensive utilization.

Waste-to-energy investment scale
By region, the scale of waste incineration treatment in key provinces and cities will increase significantly. The top five regions with the highest growth are Chongqing, Hainan, Shanghai, Beijing and Guangxi. The planned treatment scale in 2015 is 6-9 times that in 2010. From the perspective of budget investment, the budget investment for domestic garbage disposal facilities during the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period is 263.6 billion yuan, of which the total investment in the waste incineration power generation project will exceed 100 billion yuan. In the investment distribution of various provinces, Guangdong, Shandong, and Beijing are among the top three in terms of the construction of harmless treatment facilities, with an amount of 27,198,14.6 billion yuan. In addition, the total market demand for waste incineration equipment in the next 5 years is about 50 billion yuan, and the average annual growth rate of waste power generation operating income in the next 10 years is expected to reach 18%, increasing from 3.4 billion yuan in 2010 to 189 in 2020 100 million yuan.
Since 2012, the approval and launch of waste incineration power generation projects have shown an accelerating trend. According to statistics, nearly 40 projects have been signed since 2012, with a total investment of 17 billion yuan. During the 12th Five-Year Plan period, the rapid growth of the waste incineration and power generation industry has become a consensus in the market. According to incomplete statistics, there are dozens of domestic investors mainly engaged in waste incineration power generation, and the more active companies in the market include Shanghai Environmental Group Corporation, Tianjin TEDA Corporation, Jiangsu Tianying Environmental Protection Company, Chongqing Sanfeng Kawanta Environmental Industry Company, Chuangguan Environmental Protection (China) Company, Shenzhen Energy Environmental Protection Engineering Company, Green Power Holding Group Company, etc.
During the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period, the total investment in the construction of harmless treatment facilities for urban household garbage in the country was about 263.6 billion yuan, of which, the investment in harmless treatment facilities was 173 billion yuan; the investment in the construction of the operational system was 35.1 billion yuan; the investment in stock remediation projects 21.1 billion yuan; 19.3 billion yuan for the special project of restaurant and kitchen waste; 21 billion yuan for the waste classification demonstration project; 2.5 billion yuan for the construction of the regulatory system.
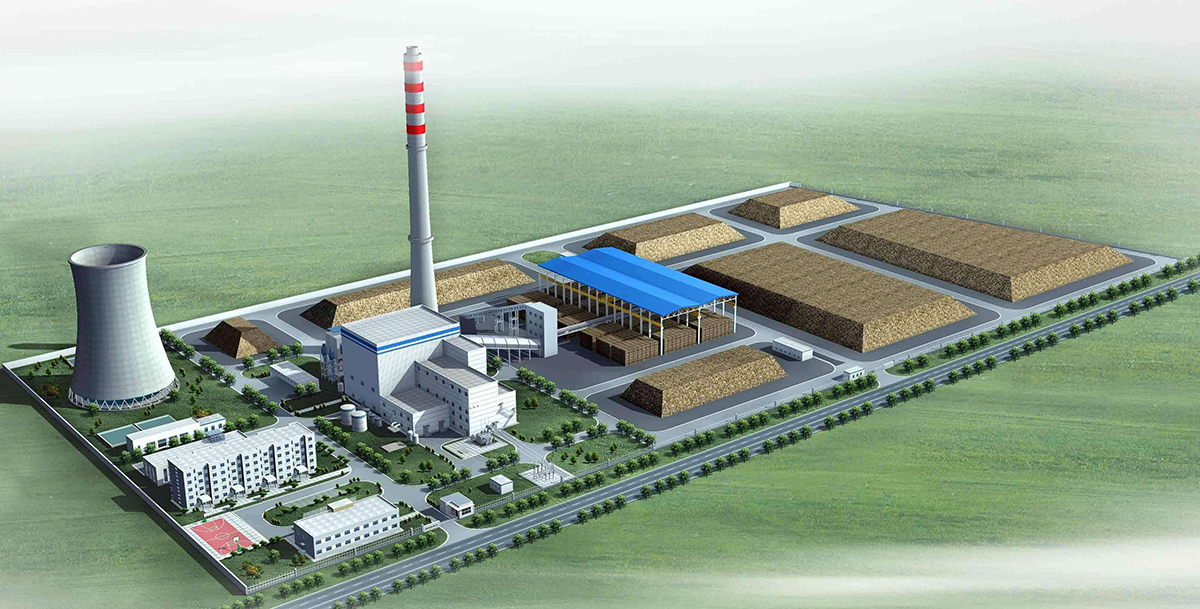

What is the prospect of waste-to-energy
2019 is the year in which my country's waste incineration power generation projects are the most constructed. There are 600 large, medium and small domestic waste incineration power plants in the country that are planned to be built, and a preliminary estimate of a single project investment is about 200 million to 2 billion. The industry believes that the waste incineration power generation industry will usher in a "big year" in the next two years, and the market size is expected to reach 100 billion yuan.
As a rising star, waste-to-energy in my country has entered a track of rapid development, and its layout nationwide is gradually shifting from first- and second-tier cities to third- and fourth-tier cities.
In 1985, my country's first waste power plant started construction in Shenzhen. At that time, it introduced the complete set of incineration technology and equipment from Japan's Mitsubishi Corporation. The daily treatment capacity of the waste power plant was only 300 tons. However, due to the high investment cost of introducing foreign technology and the low calorific value and high moisture content of my country's incinerated waste, this has also led to the slow development of my country's waste-to-energy industry in the following decades.
Until about 2000, my country's waste incineration power generation has entered a relatively rapid development stage. With the continuous development of China's economic development and urbanization level, there are more and more domestic garbage, and the urgency of construction of garbage incineration plants is also increasing. After years of precipitation, China's garbage incinerator grate technology and equipment have been From completely relying on imports, localization has been achieved, creating conditions for the popularization of domestic use, and the investment threshold for waste incineration power plants has also been greatly reduced. At the same time, with the further improvement of environmental standards, practice has proved that the original domestic fluidized bed process is not applicable, and mechanical grate furnace technology and equipment have gradually become mainstream.
Analysis of the development trend and status quo of waste-to-energy industry in 2020
As of the end of 2018, there were about 364 domestic waste incineration power plants built and put into operation in my country, with a total treatment capacity of 377,000 tons/day. Among them, there are 284 incineration power plants using grate furnaces, accounting for 78% of the total.
There are about 100 large-scale domestic waste incineration power plants projects under construction in China in 2019, and 47 in the eastern region, of which 9 are under construction in Guangdong Province, and the province’s cumulative waste treatment capacity is also the highest, about 19450 Tons/day. At the same time, waste incineration power generation projects in the central and western regions are also under intense planning and construction. Henan Province plans to build about 13 waste incineration power generation projects this year, the largest in the country, with a cumulative waste treatment capacity of 14550 tons/ day.
At present, there are less than 100 invested and operating companies in the field of waste incineration, and the total market share of the top six companies is nearly 52%, that is, more than half of the market share. The total market share of the top three companies is 39%, that is, they occupy nearly two-fifths of the market share. Hangzhou Jinjiang, as a leading enterprise in scale, has a market share of 15.38%.
From the data point of view, the total scale of the five enterprises is more than 20,000 tons. Only Jinjiang, Hangzhou, with more than 40,000 tons of daily processing projects, has a relatively large number of projects, reaching 40. There are four companies with a daily processing capacity of over 20,000 tons, namely China Environmental Protection, Green Power, Shanghai Environment, and China Everbright International.
The volume of garbage removal and transportation is huge, and it is mainly sanitary landfill. According to statistics, in 2015, the city's municipal solid waste removal volume was 192 million tons, and the municipal solid waste disposal volume was 180 million tons. Among them, the amount of sanitary landfill treatment is 115 million tons, accounting for 63.9%; the amount of incineration treatment is 61 million tons, accounting for 33.9%; other treatment methods account for 2.2%. The harmless treatment capacity of domestic garbage incineration treatment facilities is 216,000 tons/day, accounting for 32.3% of the total treatment capacity.
In 2016, the volume of domestic garbage removal in China was 20.73 million tons, a growth rate of 5.39%; the volume of harmless treatment of domestic garbage was 195.61 million tons, a growth rate of 8.59%; the capacity of harmless treatment of domestic garbage was 625,000 tons/day, The growth rate is 8.34%; the domestic garbage incineration harmless treatment capacity is 258,000 tons/day, the growth rate is 17.77%; the domestic garbage incineration harmless treatment capacity is 72 million tons, the growth rate is 16.59%; the urban household garbage is harmless The rate of chemical treatment is 95.0%, an increase of 0.9 percentage points; there are 260 non-hazardous household waste incineration plants, with a growth rate of 18.18%; in 2016, China’s waste incineration power generation capacity was 21.5 billion kilowatts, with a growth rate of 17.8%.
With the rapid development of the global economy and the improvement of material living standards, the waste-to-energy industry is increasing, and the pollution caused by garbage to the environment is becoming more and more serious. Waste incineration technology originated in the late 19th century. After entering the 1970s, due to the increase of combustible materials in the waste and the continuous improvement of industrial technology, the waste incineration technology has developed rapidly and the incineration technology has matured.

Waste-to-energy investment scale
By region, the scale of waste incineration treatment in key provinces and cities will increase significantly. The top five regions with the highest growth are Chongqing, Hainan, Shanghai, Beijing and Guangxi. The planned treatment scale in 2015 is 6-9 times that in 2010. From the perspective of budget investment, the budget investment for domestic garbage disposal facilities during the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period is 263.6 billion yuan, of which the total investment in the waste incineration power generation project will exceed 100 billion yuan. In the investment distribution of various provinces, Guangdong, Shandong, and Beijing are among the top three in terms of the construction of harmless treatment facilities, with an amount of 27,198,14.6 billion yuan. In addition, the total market demand for waste incineration equipment in the next 5 years is about 50 billion yuan, and the average annual growth rate of waste power generation operating income in the next 10 years is expected to reach 18%, increasing from 3.4 billion yuan in 2010 to 189 in 2020 100 million yuan.
Since 2012, the approval and launch of waste incineration power generation projects have shown an accelerating trend. According to statistics, nearly 40 projects have been signed since 2012, with a total investment of 17 billion yuan. During the 12th Five-Year Plan period, the rapid growth of the waste incineration and power generation industry has become a consensus in the market. According to incomplete statistics, there are dozens of domestic investors mainly engaged in waste incineration power generation, and the more active companies in the market include Shanghai Environmental Group Corporation, Tianjin TEDA Corporation, Jiangsu Tianying Environmental Protection Company, Chongqing Sanfeng Kawanta Environmental Industry Company, Chuangguan Environmental Protection (China) Company, Shenzhen Energy Environmental Protection Engineering Company, Green Power Holding Group Company, etc.
During the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period, the total investment in the construction of harmless treatment facilities for urban household garbage in the country was about 263.6 billion yuan, of which, the investment in harmless treatment facilities was 173 billion yuan; the investment in the construction of the operational system was 35.1 billion yuan; the investment in stock remediation projects 21.1 billion yuan; 19.3 billion yuan for the special project of restaurant and kitchen waste; 21 billion yuan for the waste classification demonstration project; 2.5 billion yuan for the construction of the regulatory system.

What is the prospect of waste-to-energy
2019 is the year in which my country's waste incineration power generation projects are the most constructed. There are 600 large, medium and small domestic waste incineration power plants in the country that are planned to be built, and a preliminary estimate of a single project investment is about 200 million to 2 billion. The industry believes that the waste incineration power generation industry will usher in a "big year" in the next two years, and the market size is expected to reach 100 billion yuan.
As a rising star, waste-to-energy in my country has entered a track of rapid development, and its layout nationwide is gradually shifting from first- and second-tier cities to third- and fourth-tier cities.
In 1985, my country's first waste power plant started construction in Shenzhen. At that time, it introduced the complete set of incineration technology and equipment from Japan's Mitsubishi Corporation. The daily treatment capacity of the waste power plant was only 300 tons. However, due to the high investment cost of introducing foreign technology and the low calorific value and high moisture content of my country's incinerated waste, this has also led to the slow development of my country's waste-to-energy industry in the following decades.
Until about 2000, my country's waste incineration power generation has entered a relatively rapid development stage. With the continuous development of China's economic development and urbanization level, there are more and more domestic garbage, and the urgency of construction of garbage incineration plants is also increasing. After years of precipitation, China's garbage incinerator grate technology and equipment have been From completely relying on imports, localization has been achieved, creating conditions for the popularization of domestic use, and the investment threshold for waste incineration power plants has also been greatly reduced. At the same time, with the further improvement of environmental standards, practice has proved that the original domestic fluidized bed process is not applicable, and mechanical grate furnace technology and equipment have gradually become mainstream.

Analysis of the development trend and status quo of waste-to-energy industry in 2020
As of the end of 2018, there were about 364 domestic waste incineration power plants built and put into operation in my country, with a total treatment capacity of 377,000 tons/day. Among them, there are 284 incineration power plants using grate furnaces, accounting for 78% of the total.
There are about 100 large-scale domestic waste incineration power plants projects under construction in China in 2019, and 47 in the eastern region, of which 9 are under construction in Guangdong Province, and the province’s cumulative waste treatment capacity is also the highest, about 19450 Tons/day. At the same time, waste incineration power generation projects in the central and western regions are also under intense planning and construction. Henan Province plans to build about 13 waste incineration power generation projects this year, the largest in the country, with a cumulative waste treatment capacity of 14550 tons/ day.
At present, there are less than 100 invested and operating companies in the field of waste incineration, and the total market share of the top six companies is nearly 52%, that is, more than half of the market share. The total market share of the top three companies is 39%, that is, they occupy nearly two-fifths of the market share. Hangzhou Jinjiang, as a leading enterprise in scale, has a market share of 15.38%.
From the data point of view, the total scale of the five enterprises is more than 20,000 tons. Only Jinjiang, Hangzhou, with more than 40,000 tons of daily processing projects, has a relatively large number of projects, reaching 40. There are four companies with a daily processing capacity of over 20,000 tons, namely China Environmental Protection, Green Power, Shanghai Environment, and China Everbright International.
The volume of garbage removal and transportation is huge, and it is mainly sanitary landfill. According to statistics, in 2015, the city's municipal solid waste removal volume was 192 million tons, and the municipal solid waste disposal volume was 180 million tons. Among them, the amount of sanitary landfill treatment is 115 million tons, accounting for 63.9%; the amount of incineration treatment is 61 million tons, accounting for 33.9%; other treatment methods account for 2.2%. The harmless treatment capacity of domestic garbage incineration treatment facilities is 216,000 tons/day, accounting for 32.3% of the total treatment capacity.
In 2016, the volume of domestic garbage removal in China was 20.73 million tons, a growth rate of 5.39%; the volume of harmless treatment of domestic garbage was 195.61 million tons, a growth rate of 8.59%; the capacity of harmless treatment of domestic garbage was 625,000 tons/day, The growth rate is 8.34%; the domestic garbage incineration harmless treatment capacity is 258,000 tons/day, the growth rate is 17.77%; the domestic garbage incineration harmless treatment capacity is 72 million tons, the growth rate is 16.59%; the urban household garbage is harmless The rate of chemical treatment is 95.0%, an increase of 0.9 percentage points; there are 260 non-hazardous household waste incineration plants, with a growth rate of 18.18%; in 2016, China’s waste incineration power generation capacity was 21.5 billion kilowatts, with a growth rate of 17.8%.
With the rapid development of the global economy and the improvement of material living standards, the waste-to-energy industry is increasing, and the pollution caused by garbage to the environment is becoming more and more serious. Waste incineration technology originated in the late 19th century. After entering the 1970s, due to the increase of combustible materials in the waste and the continuous improvement of industrial technology, the waste incineration technology has developed rapidly and the incineration technology has matured.
Contact Us
Resolve Your Problems within One Minute



Address:No.11 Minhe Road, Private Industrial Park, Development Zone, Kaifeng City
Inquiry
If you have any questions about our company and products, please contact us immediately. Any inquiries and Suggestions would be appreciated.
We will keep your information confidential.